India Encyclopedia:Police Rank in Indian States/Provinces
I’d been always thought that what would be the highest police authority in the states? How they know that the person next to him hold which rank? So to find out this I started to search about the different police ranks in a state. And I found that the rank list in police department is very long. Every position is associated with the different branch of rank. So I simplified the rank from higher position to the lowest one. This might be very interesting for everyone to know about the different police ranks.So is the list of police rank:
1. Director General of Police (DGP) :
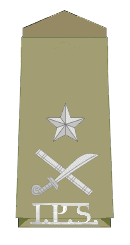
 Particularly, The highest authority of any state in police is DGP ( Director General Of Police ). In India, the Director General of Police (DGP) is a three star rank and the highest ranking police officer in Indian States and Union Territories. All DGPs are Indian Police Service (IPS) officers. The DGP is usually the head of the state police force in every Indian state. There may also be additional officers in the state who hold the rank of DGP. Common appointments for such officers include Director of Vigilance and Anti-Corruption Bureau, Director General of Prisons, Director General of fire forces and civil defence, Criminal Investigation Department (CID), Police Housing Society etc. Additionally officers who hold the rank of DGP may have commensurate appointments in central government organisations such as Director, Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), DG Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) etc. The rank insignia of a Director General of Police or Additional Director General of Police or Commissioner of Police (state) is the national emblem over crossed sword and baton.
Particularly, The highest authority of any state in police is DGP ( Director General Of Police ). In India, the Director General of Police (DGP) is a three star rank and the highest ranking police officer in Indian States and Union Territories. All DGPs are Indian Police Service (IPS) officers. The DGP is usually the head of the state police force in every Indian state. There may also be additional officers in the state who hold the rank of DGP. Common appointments for such officers include Director of Vigilance and Anti-Corruption Bureau, Director General of Prisons, Director General of fire forces and civil defence, Criminal Investigation Department (CID), Police Housing Society etc. Additionally officers who hold the rank of DGP may have commensurate appointments in central government organisations such as Director, Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), DG Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) etc. The rank insignia of a Director General of Police or Additional Director General of Police or Commissioner of Police (state) is the national emblem over crossed sword and baton.
2. Additional Director General Of Police (ADGP) :
In India the Additional Director General of Police (ADG) is a 3 star rank, the highest ranking police officer in Indian State and Territories. All ADGs are Indian Police Service (IPS) officers. The equivalent position or designation in the state governments or federal government are Commissioner of Police, special or additional secretary and Cabinet Secretariat. The rank insignia of an ADG is the national emblem over a crossed sword and baton.
3. Inspector General Of Police/ Special Inspector General Of Police (IGP/SIGP) :
An Inspector General of Police or Inspector-General of Police is a senior officer in the police force or police service of several nations. The rank usually refers to the head of a large regional command within a police service, and in many countries refers to the most senior officer of the entire national police.
4. Deputy Inspector General Of Police (DIGP) :
Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIG) or Additional Commissioner of Police is a one-star rank in the Indian Police Service (IPS). The officer holding this rank is above a Senior Superintendent of Police or Deputy Commissioner of Police and under an Inspector General of Police or Joint Commissioner of Police. It is roughly analogous to the ranks of commander and assistant chief constable in the UK police service.Asper protocol the DIG rank of police is above the rank of Lt Col and below the rank of a Col of the Army.
5. Superintendent of Police/Deputy Commissioner Of Police (SP/DCP) :
In India, a District Superintendent of Police (SP) or Deputy Commissioner of Police (DCP) heads the police force of a district. Superintendents of Police are officers of the Indian Police Service. They are entrusted with the responsibility of maintaining law and order and related issues of a district of a state or a union territory of India. They are assisted by the officers of the State Police Service and other State Police officials. Their rank badge is the State Emblem above one star, although those selected for higher rank or with fifteen or more years’ service wear the State Emblem above two stars. The rank below it is Additional Deputy Commissioner of Police (ADL.DCP) or Additional Superintendent of Police (ASP), while the rank above it is Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP) or Additional Commissioner of Police (ACP). The rank of superintendent of police is equivalent to the rank of lieutenant colonel of the Indian army.
6. Superintendent of Police/Deputy Commissioner Of Police (Junior Management Level)
Work same as SP.
7. Additional Superintendent Of Police/Deputy Commissioner of Police (ASP/DCP) [Less than 10 years of service]
Additional Superintendent of Police or Additional Deputy Commissioner of Police (Addl. S.P. or Addl.D.C.P.) is still in use in India where the officer holding this rank can be from Indian Police Service or from Indian States Police Services like West Bengal police Service(W.B.P.S.),Odisha Police Service(O.P.S.), Maharashtra Police Service(M.P.S.) etc.The rank above it is Superintendent of police (S.P.) or Deputy commissioner of police (D.C.P.), and the rank below it is Deputy superintendent of Police (Dy.S.P. / D.S.P. ) or A.C.P.(Assistant Commissioner of Police)
8. Deputy Superintendent of Police/Assistant Commissioner Of Police (DSP/ACP) :
In India, senior officers of the rank of assistant superintendent/assistant commissioner of police or above may belong to the national Indian Police Service or state police services, whereas Indian inspectors and constables belong to the individual provincial police forces.The rank of Assistant Commissioner is also used in Indian Income Tax, Customs, Central Excise and Service Tax Administration, as an officer of Indian Revenue Service.
9. Police Inspector (P.I.) :
Inspector is both a police rank and an administrative position, both used in a number of contexts. However, it is not an equivalent rank in each police force.
10. Assistant Police Inspector (A.P.I.) :
Inspector is both a police rank and an administrative position, both used in a number of contexts. However, it is not an equivalent rank in each police force.
11. Police Sub-Inspector (SI) :
A sub-inspector (SI) is generally in command of few police personnel (with head constables, the equivalent of corporals, commanding police outposts). He is the lowest ranked officer who under Indian Police rules and regulations can file a charge sheet in court, and is usually the first investigating officer. Officers subordinate to him cannot file charge sheets, but can only investigate cases on his behalf.
12. Assistant Police Sub-Inspector (ASI) :
In the police forces of India, an assistant sub-inspector (ASI) is a non-gazetted police officer ranking above a police head constable and below a sub-inspector. The rank insignia for an ASI is one star, and a red and blue striped ribbon at the outer edge of the shoulder straps.
13. Head Constable (HC) :
Head constable in the Indian police is equivalent to sergeant in police forces in other countries. Head constables wear three point-down chevrons on their sleeve or three bars on their epaulettes.
14. Police Constable (PC) :
Police Constable (abbreviated PC) is the lowest police rank in India followed by Head Constable. General law and order being a state subject in India, each state government recruits police constables. A Police Constable has no shoulder insignia while a Head Constable has one strip or one Chevron depending upon the state. All senior officers are Indian Police Service officers appointed through Civil Services Exam. Since each state has its own police force, the uniforms and insignia of the police varies, though the rank structure is same. The central paramilitary forces under the Ministry of Internal Affairs also maintains the same ranks as state police even though their jurisdiction varies considerably.All the POLICE constable wear (khaki)coloured uniform which indicate that he/she is a police officer. Police Constables in India have been seen in possession of guns but their ability to use them is known to be subjected to authorization passed by the chain of command in the police force.












Post a Comment